T2DM, a pandemics
with still huge unmet
medical needs
THAC aims to change the way patient care and healthy aging are addressed. THAC is primarily focused on Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (incl. prevention of complications), a condition with still unmet medical needs, as identified by health agencies.
Still a large unmet medical need as claimed by healthcare authorities



THAC therapeutic solution addresses insulin resistance, the root cause of T2DM as requested by healthcare authorities
ALF-5755, the active ingredent of THAC drug candidates for T2DM, is targeted the root cause of the disease by tackle the apperance of insulin resistance all along the disease, and by acting directly to the gut microbiota in order to restore the dysbiosis.
Thanks to its unique and innovative properties against local inflammation and local oxidation, ALF-5755 is also able to decrease and to prevent side effects and complications related to T2DM and age-related diseases.
T2DM is the first non-infectious pandemics in the world and the first killer (WHO)
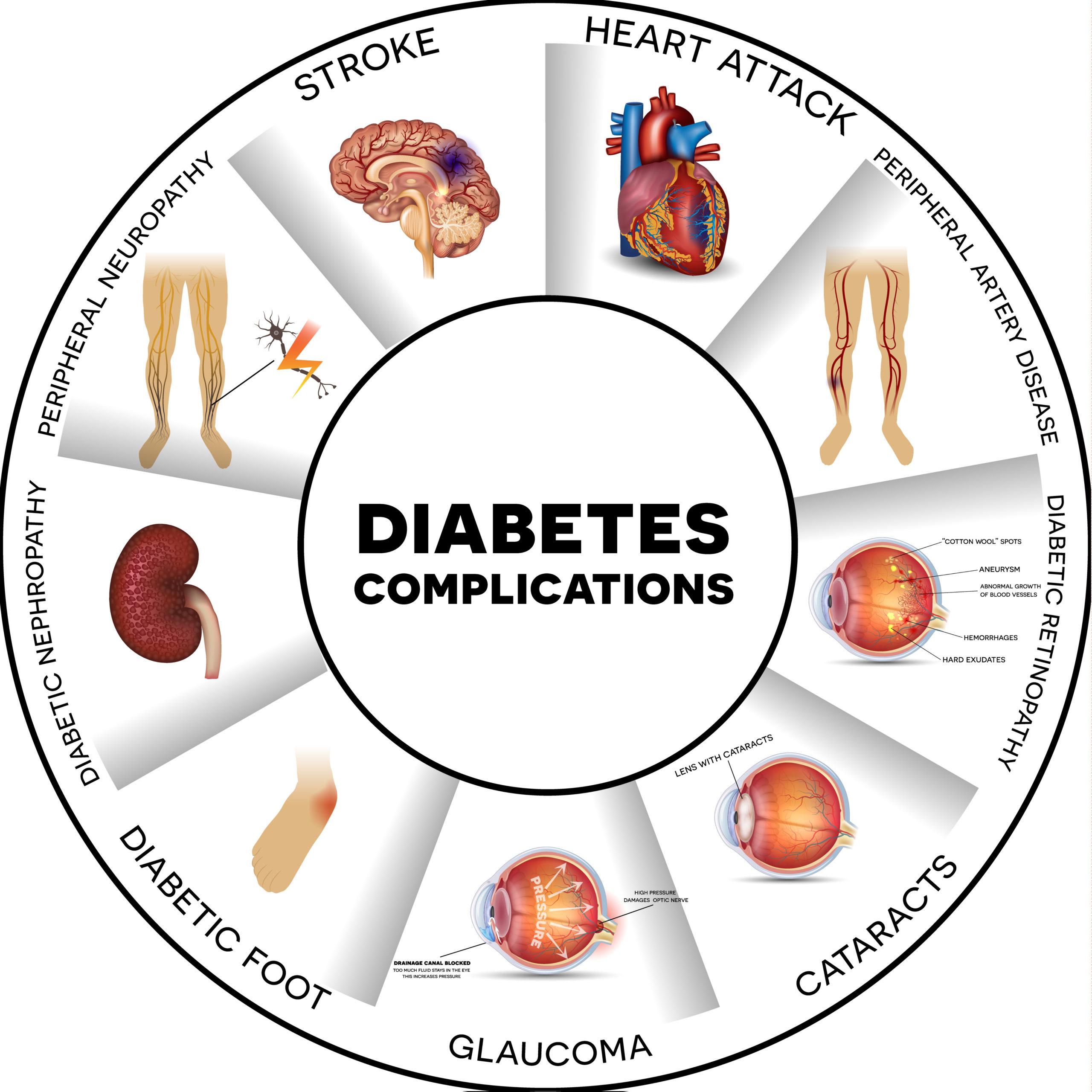
Despite existing therapeutic solutions, Type 2 diabetes is a chronic age-related disease which will concern up to 750 million patients by 2040 (+51% from 2019). One adult out of 10 will be affected by the disease by mid-century. The quality of life of the patient is highly degraded, their life expectancy is reduced up to 10 years with severe complications, and the disease is responsible of one death every 6 seconds in the world.
Amongst the severe complications, the diabetic foot wound is considered as a medical urgency with a drastic evolution towards foot ulcers and amputation. Up to 25% of the diabetic patients is concerned. Due to the fact that there is no adapted prevention and treatment, one lower limb amputation is observed every 30 seconds in the world, in the context of the T2DM.
T2DM is also an economic burden on patients and healthcare machinery around the globe. The market is going to be doubled between 2016-2026 and the total available market including pre-diabetes is reaching several hundreds of million dollars. Worldwide associated costs are expected to reach around £1000 bn in 2045. Additional costs related to the severe complications have to be included. – Ceed diabetes 2020, Diabetologica 2020, J Epid Global Health 2019.
The need of new drugs for T2DM targeting the root cause of the disease
Therapeutic progress in T2DM has been achieved with 4 main classes of products, usually prescribed in bi- and tri-therapies, and based on different modes of action for controlling glycemia. But despite these therapeutic achievements, T2DM has still an ineluctable evolution in most patients. The adaptation of the treatment is mandatory all along the progression of the disease. the death of patients is still pre-matured, and severe complications of the disease are not prevented. In that context, WHO and international diabetes associations claimed the need of new drugs which present the following features (WHO T2DM Global Report).
ALF-5755, the active ingredient of THAC, tackle insulin resistance thanks to its unique and innovative mechanism of action


